DGrid's Solution: Core Architecture and Key Modules
INFO
DGrid.AI = Decentralized Routing & Verification Network + LLM & Agent Free Market + AI DAO Governance System
DGrid.AI addresses the critical gaps between Web3 AI and centralized AI through an interconnected ecosystem composed of nodes, protocols, and decentralized infrastructure.
By integrating standardized AI RPC interfaces, distributed inference nodes, intelligent routing, on-chain settlement, and secure storage, we have built a trustless, scalable, and user-centric LLM and Agent service network—enabling AI to become a native capability of blockchain applications. At its core, DGrid’s solution redefines decentralized AI inference through three foundational components: distributed nodes for model execution with result trustworthiness guaranteed by Proof of Quality (PoQ), standardized protocols for universal access, and on-chain mechanisms for full transparency.
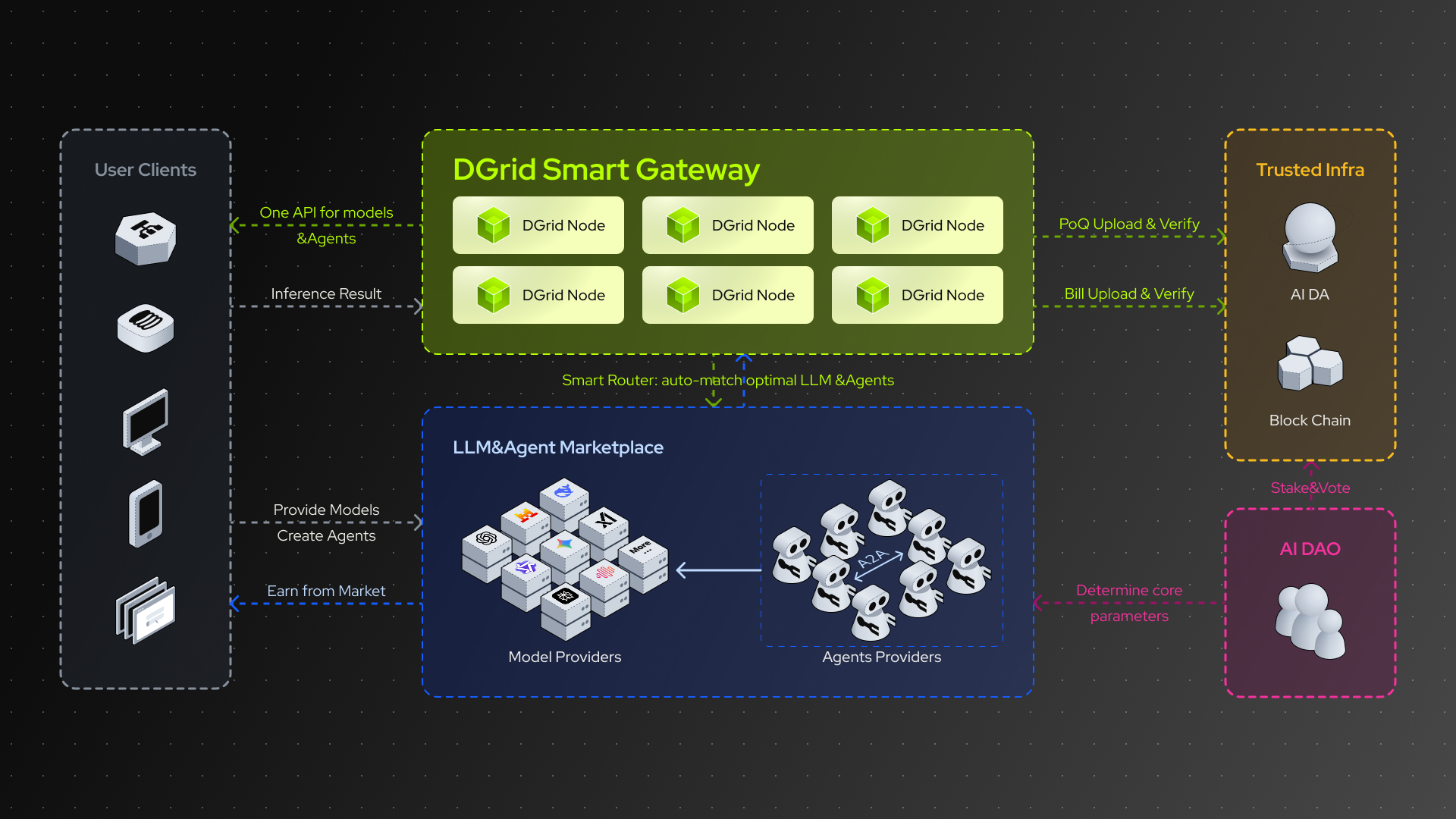
1. Decentralized Routing & Verification Network
- Unified Intelligent Access: Provides developers with a single API to access thousands of specialized models and preconfigured Agents simultaneously, significantly reducing integration costs.
- Intelligent Routing & Scheduling: Automatically recommends and schedules optimal service resources based on multi-dimensional metrics including task type, budget constraints, and historical performance data.
- Trusted Verification Mechanism: Leverages the Proof of Quality (PoQ) algorithm to ensure the trustworthiness of AI and Agent workflows and output results, achieving efficient, censorship-resistant, and traceable services.
2. LLM & Agent Free Market
- Open Listing Opportunities: Model providers, AI developers, and prompt engineers can list fine-tuned models or customized Agents on the DGrid network, set their own prices, and earn revenue directly from global users through a transparent competition mechanism.
- Value Tokenization: High-quality models and Agents can be tokenized on DGrid to capture long-term market value.
3. DGrid Nodes: Decentralized Inference Execution
DGrid Nodes are community-operated nodes that form the computational core of the network by hosting one or more Large Language Models (LLMs, e.g., Llama-2, Mixtral) and AI Agents. These nodes:
- Execute inference tasks for users, process inputs (e.g., text prompts, smart contract queries), generate outputs via preloaded models, and verify inference result quality through the PoQ (Proof of Quality) mechanism to ensure output trustworthiness and accuracy.
- Adapt to hardware capabilities: Operators can select models matching their server specifications—ranging from lightweight 7B-parameter models on basic GPUs to 70B+-parameter models on high-performance hardware.
- Report real-time metrics (latency, Compute Unit [CU] consumption) to the DGrid network, providing data support for intelligent routing and enabling optimized task allocation.
By distributing inference tasks across thousands of independent nodes, DGrid eliminates single points of failure and ensures geographic redundancy—critical for Web3 applications requiring 24/7 reliability.
4. DGridRPC: Universal Access & Request Verification
- DGridRPC: A standardized JSON-RPC protocol that simplifies user access to models and Agents in the network. It provides a unified API for invoking any LLM or Agent (regardless of node or model type) and integrates EIP-712 signatures to verify user requests—ensuring only authorized and pre-paid tasks are processed.
DGridRPC resolves the "interface fragmentation" issue in Web3 AI, making LLM and Agent integration as straightforward as calling a smart contract.
5. Proof of Quality (PoQ): Trust Guarantee for Inference Results
Proof of Quality (PoQ) is the core mechanism in the DGrid ecosystem that ensures the trustworthiness of LLM inference and Agent execution results. Working in tandem with distributed nodes and DGridRPC, it forms a closed-loop "Request-Execution-Verification" workflow:
- Multi-Dimensional Quality Assessment: PoQ objectively scores inference results generated by DGrid Nodes based on three key dimensions: accuracy alignment (comparison against standard answers or reference results), response consistency (output deviation of the same request across different nodes), and format compliance (adherence to user-specified output requirements). The evaluation framework further incorporates cost-efficiency considerations and semantic similarity verification logic to balance high quality with low overhead.
- On-Chain Verifiable Proof Generation: After completing an inference task, nodes upload inference process logs and PoQ score data to the network to generate tamper-proof quality proofs. Users can query these proofs on-chain to quickly verify result reliability without re-executing inference tasks. Combined with a hybrid verification architecture, this mechanism achieves low latency and low cost while ensuring computational integrity.
6. Billing Contracts & AI DA Layer: On-Chain Transparency
- Billing Contracts: Smart contracts deployed on the blockchain for automated $DGAI token settlement between users and nodes. These contracts calculate fees based on Compute Units (CU) and latency, deduct payments from user accounts via the x402 protocol, and distribute rewards to node operators—eliminating intermediaries.
- AI DA Layer (Data Availability): A decentralized storage network where all inference request data is secured by PoQ to ensure auditability. Users can verify billing details, and nodes can prove task completion, thereby increasing transparency for dispute resolution or compliance audits.
7. Security Mechanisms
DGrid.AI has established a comprehensive security framework to ensure trustlessness in the decentralized network, combining technical safeguards with on-chain transparency:
Trusted Inference Environment
- Immutable Runtime: DGrid Node operators cannot modify the weights or execution environments of Large Language Models (LLMs) and AI Agents, ensuring consistent model behavior across the network.
- Resource Controls: Strict limits on CPU, GPU, and network usage (enforced by nodes) prevent Denial of Service (DoS) attacks.
On-Chain Auditing & Accountability
- Tamper-Proof Records: All critical activities—node registration, inference metadata (inputs/outputs), fee settlements, and rewards—are recorded on-chain via Billing Contracts and stored in the AI DA Layer.
- Automatic Penalty Mechanisms: The DGrid network monitors node behavior; malicious actors (e.g., submitting false results) face penalties such as confiscation of staked tokens or node blacklisting, enforced by smart contracts.
- Decentralized Governance: $DGAI token holders can vote on protocol upgrades, fee structures, and security parameters, ensuring network development aligns with community interests.
Core Advantages: Defining the Next-Generation AI Infrastructure
By integrating decentralized execution, intelligent coordination, secure inference, and transparent settlement, DGrid builds core advantages that distinguish it from traditional centralized AI and existing Web3 AI solutions—redefining the next generation of AI infrastructure:
- End-to-End Trustworthiness: Based on PoQ quality proofs and on-chain evidence storage, it achieves verifiable and auditable inference processes and results, solving the "black box" problem.
- Seamless Integration Experience: A single DGridRPC interface is compatible with thousands of models and Agents, significantly reducing developer integration and migration costs.
- Ecosystem Fairness & Win-Win Collaboration: The open LLM & Agent Free Market and merit-based incentive mechanism ensure value alignment among creators, builders, and users.
- Elasticity & Resilience: The distributed node network eliminates single points of failure, and geographic redundancy guarantees 24/7 service availability, resisting regional outages and regulatory risks.
- Community-Driven Autonomous Governance: AI DAO drives network evolution; $DGAI holders lead key decisions, and AI Agents can participate in automated governance on behalf of users, ensuring ecosystem development aligns with community interests.
